Introduction of CNG
Have you ever wondered what makes Compressed Natural Gas (CNG) an environmentally friendly alternative to traditional fuel?
CNG natural gas is under constant pressure, clear and odorless. This means that CNG is not only friendly to our rich natural world, but can also be used as an alternative to saving.
What is CNG?
CNG stands for Compressed Natural Gas is a mixture of gases such as Methane, Ethane, propane, butane, co2, etc.
The major constituent being Methane it is found dissolved in petroleum or in a huge amount under Earth surfaces in oil and gas bearing areas.
In India, its resources exist in Bombay-Offshore, Upper-Assam, Krishna, and Godavari basins, and Gujarat.
Refineries are a secondary source of nature has where the dissolved gases in crude oil are released during the refining process but in laser volumes.
Composition of CNG (%volume)
| Methane | 93.20 |
| Ethane | 4.27 |
| Propane | 1.38 |
| i-Butane | 0.18 |
| n-Butane | 0.20 |
| i-Pentane | 0.04 |
| n-Pentane | 0.03 |
| Hexanes | 0.00 |
| Carbon dioxide | 0.27 |
| Nitrogen | 0.43 |
| Moisture content | 2.0ppm |
Increased power & efficiency in CNG Engine
CNG is a safe fuel being lighter than air is diffuses easily into the atmosphere and does not form a sufficiently rich mixture from combustion to take place.
In this respect CNG is superior to LPG or propane or even petrol storage of propane on the vehicle is not as difficult as CNG but the cost of propane is lighter than that of CNG.
The excellent knock resistance property of CNG allows the use of a higher compression ratio for increased power output and fuel economy compared to petrol.
The energy content per kg of CNG is very similar to that the petroleum-based fuel but it has a lower energy content per unit of volume.
Due to its anti-knock property, CNG can be safely used in an engine with a compression ratio as high as 12:1 compared to normal petrol (range of 7.5:12 to 10:1).
At this high compression ratio, natural gas fitted engines have higher thermal efficiency than those fueled by gasoline.
CNG has a higher octane number than petrol and it is, therefore, possible for CNG engines to operate at a higher compression ratio than petrol engines without knocking.
The fuel efficiency of a CNG engine is there for better than that of a petrol engine.
However, compared to diesel engines the compression ratio is lower for CNG engines and consequently, the fuel efficiency of CNG engines is about 10 to 20% lower than that of diesel engines.
CNG presents more cost-effective emission reduction measures than quite a few other options that have been the subject of serious debate in recent months.
One of these options is the catalytic converter which cannot reduce the portion of the particular referred to as soot for diesel engines particularly.
Further and the reliability of the diesel catalytic converter has yet to be proven because of the higher sulfur content in the Indian diesel fuel.
The particulate trap is a high-cost device that is now under development of diesel engine and the process of generation of the trip to clean the disposal it carbon particle call of energy consumption and the possibility of pollution during regeneration.
Thus particulate traps are costly to install and costly to operate and maintain CNG engines over a better solution to eliminate particulate.
The importance of cost-effective efficient easy to maintain and user-friendly solutions to every come environmental problem cannot be over-emphasized, and CNG meets these requirements.
Why we should use CNG in India?
With its lower and emission levels and other advantages over existing fuels.
CNG is ideally suited to become the fuel of urban India it is especially ideal for Indian cities because:
The pipeline system required for distribution is easier to provide in cities than in rural areas.
The major portion of Indian vehicles is in the cities.
Capital for providing CNG engines is also more easily available in an urban setting.
There is adequate mechanical expertise available in the cities.
Introduction to exhaust emission combustion
Complete combustion of CNG results only in the harmless substance carbon dioxide (CO2) and water vapor (H2O).
Engine exhaust has also contained products of incomplete combustion such as carbon monoxide (CO) and partially combusted or non-combusted hydrocarbon (HC).
In addition, to nitrogen in the induction combustion air, the exhaust has also contained the oxidation product of Nitrogen (NOX).
The emission of solids particulate emission is very low on Spark-ignition engine by comparison with a diesel engine and is negligible.
Owing to the minimum sulfur content of the CNG only a very slight amount of harmful sulfur dioxide is contained in the exhaust gas of the spark-ignition engine.
Characteristics of CNG gas
-Higher octane rating (120-130) excellent knock resistance.
-lower rate of combustion pressure rise and low peak cylinder pressure.
-Energy content per kg of CNG is similar to petroleum-based fuels.
-Self-ignition temperature is 730°C about 250°C higher than Petroleum.
-CNG has very narrow flammability limits.
-Lighter than air diffuses upwards.
-Clean burning fuel exhibits no measurable black smoke very low particulate and about 40% reduction in mass emissions.
Changes made to adopt CNG Engine
Module 1 (Engine)
| Piston | Combustion bowl volume increased to reduce the compression ratio to 11.5:1. |
| Cylinder head | Spark plug introduced in place of injectors with proper threading arrangement. |
| Distributor drive | Distributor introduced in place of fuel injection pump with the adoption of drive arrangement. |
Module 2 (Engine)
| Gas feeding system | Gas inducted into the engine bike carburetor after reducing the gas pressure the stoichiometric air/fuel ratio maintained by a closed-loop system |
| Ignition system | To provide electrical Spark initiate ignition or air-fuel mixture |
| End speed Governing system | Governs the maximum speed off the engine by controlling gas the quantity inducted |
Gas storage & filling
Gas cylinder with individual manual shut off valve each cylinder has individual manual shut off valve.
Capacity
| 12*50l | For DTC |
| 8*50l, 4*95l | For BEST |
| Working pressure | 200kg/cm² |
| Test pressure | 330kg/cm² |
Filler valve
It is basically to feel the gas from the filling station with a built-in non-return valve.
Gas filling arrangement
For the faster feeling of cylinder 3. The feeling arrangement adopted.
Pressure gauge
It is the analog pressure gauge installed in the gas line graduate both in PSI and bar (0-3500 psi/ 0-250 bar).
Pressure sensor
It senses the gas cylinder pressure and communicates to an indicator on the driver’s dashboard pressure indicators of dashboards consists of four green bulbs and one red bulb the illumination of this bulb indicates the pressure level as given below:
| 4Green full | 170-200bar |
| 3Green 3/4 | 150-165bar |
| 2Green 1/2 | 110-145bar |
| 1Green 1/4 | 35-70bar |
| Red Nil | <30 bar |
Caution:- If the red bulb glows it is suggested that the vehicle needs to be taken to the nearest filling station for recharging cylinder with has to 200-bar pressure.
Gas service components
First stage regulator–
The high-pressure regulator reduces the pressure of the gas from 200 bars to 12 to 12 to 30 bars.
Normally the high-pressure regulator is set at the manufacturing and should not be adjusted in the field.
Improper installation may damage property/life.
Low pressure solenoid switch (24V)–
Located between the regulator operated by ignition switch when the valve is open gas passes from 1st stage to 2nd Stage regulator.
Caution: No repair/dismantling is recommended replace the unit is necessary.
Second Stage regulator–
It has three compartment:-
- Diaphragm chamber
- Secondary value chamber
- Primary wallpaper chamber
Functions–
(A) Reduces pressure from 13 bar to 1.04 bar absolute (which is slightly above atmospheric pressure)
(B) Used for and speed governing of 2900/3000 RPM. by receiving signals from 3 way solenoid valve which is actuated by ESG unit.
Carburetor–
All components of carburetor system except carburetor and regulator second stage regulator requires no overhauling only placement.
Gas carburetor because of its simplicity is unlikely to give any problems when properly installed with an adequate supply of gas.
Oxygen sensor–
The oxygen sensor is located between the engine exhaust manifold and catalytic converter rich air-fuel ratio supply fuel to mix with all the oxygen entering the engine.
A rich air-fuel ratio creates low oxygen levels in the exhaust because access fuel mixes with all the oxygen entering the engine.
when the lean mixture is used oxygen level in the exhaust also remains high.
The presence of unburnt Hydrocarbons in exhaust with oxygen would harm the life of the catalytic converter as well as result in emission.
The heated oxygen sensor the oxygen available in the exhaust.
Closed loop control–
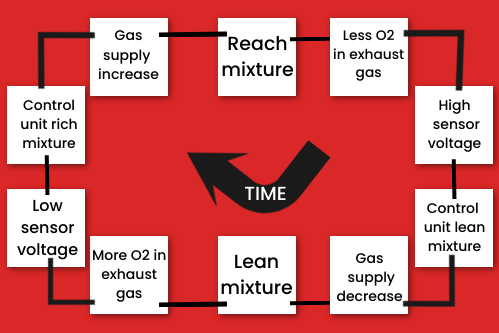
The voltage from the oxygen sensor is fid to the engine management electronic control unit (ECU).
When the ECU is reading a high voltage indicating a rich mixture is respond by reducing the gas supply duration slightly to weaken the mixture.
As the mixture weakens the oxygen sensor voltage goes low and so the ECU enriches the mixture.
By constantly increasing and then reducing the mixture strength the air/fuel ratio is kept at 17:1.
To prevent the mixture from swinging between rich and lean the ECU contains an integrator circuit that has the effect of averaging out the oxygen sensor readings.
Commander–
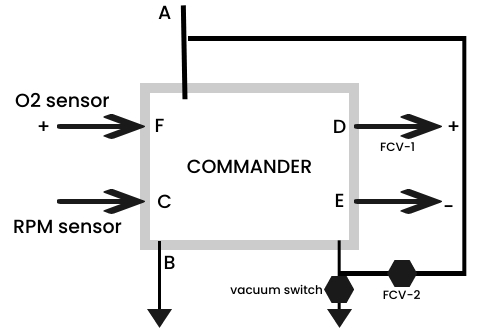
The commander basically a microprocessor that gets two input signals (1) the RPM signal from the ignition coil negative and (2) another signal from the oxygen sensor is proportional to the oxygen availability in the exhaust pipe.
Depending upon the signals the fuel delivery into the engine will be verified by regulating the vacuum stage regulator by FCV-1.
Restrictor–
The restrictor is incorporated in between the 2nd Stage regulator and 3-way valve after the T piece.
As the name implies it restricted the flow of vacuum signal from carburetor to 2nd Stage regulator for faster response.
This is necessary for reaching an effective signal from FCV 1 to 2nd Stage regulator which in turn respond in regulating gas supply to the carburetor.
Vacuum control switch–
The vacuum control which census the air intake manifold vacuum and the vacuum levels reach below 3 inches of mercury the valve will become operational.
As the valve opens the commander circuit will be bypass and 2nd fuel control valve will be actuated.
CNG Ignition system
Ignition coil–
The ignition coil consists of metal housing which accommodates primary and secondary coil on and off the primary current will induce a secondary voltage.
Distributor–
This is the contactless distributor that provides the RPM signal to the trigger box and also distributes High tension voltage to the individual spark plug.
The HT connection of the spark plug will be as per firing order.
Trigger box–
That trigger box provides the making and breaking of the primary current of the ignition coil.
The sensing of the RPM of the engine is from the signal from the ignition distributor.
This does the function of the contact breaker of the conventional distributor.
Spark plug–
This is the ignition source of the air-fuel mixture.
The secondary voltage developed by the ignition coil discharged in between the central and ground electrode of the spark plug as a spark.
The initiation of combustion cricket only is a spark plug.
Warning: In any CNG engine fitted miss firing or miss firing expert in the cylinder will head to catalytic converter damage.
End speed governor-24V
Auto relay/ESG–
The ESG unit senses the engine RPM from the ignition system signal and activates the Three-Way valve for controlling the engine RPM on failures of ESG unit the engine cannot be started on Rises beyond buying on specified RPM.
Three way solenoid–
The 3-way valve is part of an end speed governing circuit this valve is actuated by a solenoid which obtains a signal from the ESG unit depending upon the engine RPM.
Of the three ways, one is the outlet the remaining two inlets are selectively connected to the outlet depending upon the ECG signal received.
CNG Lubrication system
| Description of the system | Pressurized lubrication |
| Lubrication reservoir | Beneath crankcase |
| Feed system | By pump |
| Oil cooler | Plate type |
Electrical power circuit components
Battery–
The battery in the electrical system performs the function of a chemical storage device for electrical energy generated by the alternator the lead sulphuric acid battery is used for this purpose.
Isolation switch–
By switching off the switch both the battery terminals circuit in enterally cut off from the vehicle electrical circuit.
This situation is essentially required whenever repair work is being carried out in the electrical system this is situated near the driver seat who can easily operate this manually.
In case a vehicle is not operating for more than a day then switching off the regulations which battery discharge can be avoided.
Ignition switch–
Ignition switch when is on position supplies current for Spark generation.
Starting and charging circuit-
A starter switch relay a Starter Motor and alternator with charging circuit incorporated in CNG engine is similar to the other vehicle
24v/12V converter–
This necessity of 12V supply for ignition and closed-loop system components need the battery voltage of 24V converted to 12V the converter supply power to the following circuits.
- Ignition system
- Closed-loop system
- Gas level indicator
Do’s and Don’t for CNG Engine
Don’t
- Allow misfiring and misfiring to be analyzed immediately and rectify.
- Use open fire for detecting gas leakage.
- Are the wires to check the electrical continuity/voltage.
- Temper the fuel setting to the carburetor and 2nd Stage regulator.
- Try to reassemble and reuse gas components except for the 2nd Stage regulator and carburetor.
- Set the idling RPM in cold condition.
- Try to service filter valves.
- Temper any electrical circuit particularly the engine wiring harness.
- Make any cut and join in the wires.
- Hammer on components for fitment particularly HT cable distributor and drive for distributor components.
- Rise engine speed beyond 2000 RPM in the vehicle.
- Remove spark plug in hot/warm engine condition.
- Apply grease/oil while assembling the O2 sensor.
- Open the gas line under pressure.
- Adjust ignition timing without stroboscope.
DO’s
- Cng engine carries out all the maintenance as per the maintenance schedule.
- Use correct spanners and tools to avoid damage to the engine-related system.
- Check all gas leak joints only with a soap solution.
- Check all electrical components and voltage only with a multimeter.
- Replace washers/ferrules rules of the gas circuit on removal.
- Maintain the ignition timing as per specification.
- Avoid spillage/leakage of coolant lubricating oil.
- Maintain correct coolant lubricating oil level and connection particularly horse clips intact.
- Proper routing of wires (during reassembling of components) if possible in the original route.
- In the use of CNG engine, correct procedure for dismantling and assembling of component unnecessary hitting or force-fitting will damage the component.
- Spark plug to be removed and fitted only with spark plug sleeve clamp in position.
We hope readers can understand this “What is CNG? and Why we should use CNG in India?” article and basic fundamentals of a CNG engine system.
Read this:- Fuel Supply System in Petrol Engine [Spark Ignition Engine]
Visit site:- www.carsuffer.com






Comments on “What is CNG? and Why we should use CNG in India?”