Learn about the fuel supply system in the petrol engine and the components are attached to the fuel supply system in the petrol engine.
CARSUFFER.COM
What is the fuel supply system in the petrol engine?
In the petrol engine, the fuel supply system is made up of a fuel tank, pump, filter, injectors or carburetor, and is responsible for delivering the fuel to the engine as needed.
Each component must perform seamlessly to achieve the expected performance and reliability.
Petrol from the fuel tank has to be filled into a carburetor so that it can be mixed with air for onward feeding to the cylinder.
Fuel is fed to the carburetor in two ways namely:
- Gravity feed system
- Forced feed system
Gravity feed system
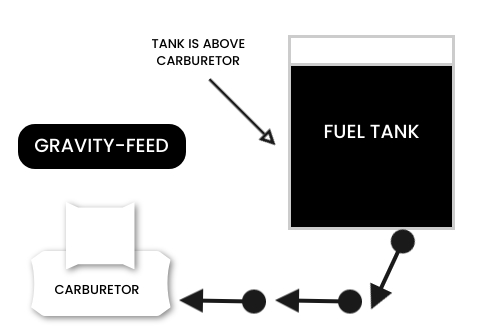
In this fuel supply system in the petrol engine, the fuel tank is placed above the level of the carburetor and is connected to it with the help of pipe fuel flows to the carburetor due to its own gravity.
Such a system is not used in a motor vehicle as there is no place to keep the tank at a higher level however this system is used in almost all the motorcycle and scooters being it very cheap.
Forced feed system
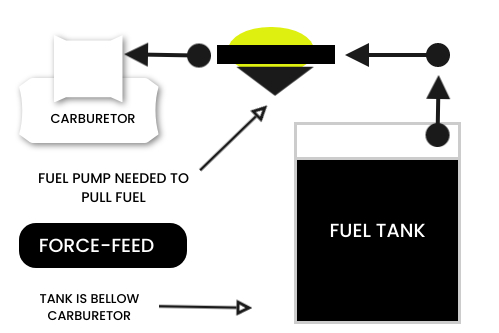
In this fuel supply system in the petrol engine, the tank is placed at a distance and also under the level of the carburetor to pump the fuel from low level and feed it to the carburetor fuel pump is used. In almost all the vehicle this system is used.
Components of fuel supply system in petrol engine
The main part of the fuel feed system is employed in a motor vehicle are shown below:
- Fuel-tank
- Fuel-filter
- Fuel-pump
Now let’s talk about the construction and operation of these units.
● Fuel–tank
It is made of galvanized MS sheet and is fast and under the chassis with straps nuts and bolts with rubber packing in between.
Petrol connection is taken at the bottom sometimes a fine wire gauge strainer is also fitted in it so that petrol leaving the tank is free from coarse suspended impurities.
The drain plug is fitted at the lowest portion of the tank sometimes plug position of the tank is dished so that condenser water being heavier than petrol can settle here.
In a rainy season, this condensed water should be drained by opening the drain plug at regular intervals the fuel tank has 2/3 compartments interconnected with each other.
This compartment is made in the bank so that fuel does not strike the walls of the tank when the vehicle is moving on a rough road.
Fuel-tank has a neck made on top of it where a cap is attached to the neck and a small bleed pipe is also inserted so that when the fuel is consumed the space left by the gasoline is filled with air.
In some vehicles instead of providing a ventilator, the cap is drilled.
● Fuel–filter
In some of the fuel, pump strainer is placed in the glass bowl it requires cleaning at each service.
In some of the vehicle, a separate fuel filter is connected between the carburetor and fuel pump this glass bowl and the filter element should be cleaned and each service.
While in some other makes the inline type of filter this type of filter is not cleanable and has to be replaced when found dirty.
The fuel filter fitted in Japanese engine is not cleanable type hence complete assembly has to be changed at 40,000 kilometers.
While fitting the filter and sure that the outlet coming on top and inlet is at the lower end of the body.
● Fuel pump
The function of the fuel pump is to pump fuel from the tank and feed it to the carburetor.
These pumps are designed to pump a sufficient quantity of fuel at all working conditions so that the pipeline always remains filled up with fuel at all working conditions failing which these are chances of vapor lock usually called airlock in the pipeline.
There are two types of pump used these are:
- Electrical fuel pump
- Mechanical fuel pump
Electric fuel pump
In some of the vehicles instead of mechanical fuel pump electrical fuel pump is fitted which is connected through an ignition key, there are two types of pump available these are:
- Diaphragm type
- Bellow type
Diaphragm type
While the other is earthed through a contact point. when we switch on the ignition switch, the electric current flows in the coil generating a magnetic field. due to this magnetic field, a plunger in the coil is pulled up.
This plunger is connected to the diaphragm with the result it also gets lifted up. due to the lifting of the diaphragm, a vacuum is created in the chamber below the diaphragm, which opens the inlet valve and sucks the petrol from the tank and the chamber gets filled up.
When the plunger lifts up it connects the electric contact with the result electric current is switched off and the effect of the magnetic field in the coil diminishes the spring fitted over the diaphragm pushes the diaphragm down along with the plunger thus pushing the petrol out from The Chamber through the outlet valve.
As soon as the plunger comes down the electric contact point open the current again flows into the coil. due to the magnetic effect, the plunger again lifts up along with the diaphragm, and the pump works in the same way.
In case no petrol is required by carburetor the diaphragm remained lifts up with open contact. as no current is following it remains to lift it up but as soon as petrol is taken by the carburetor the spring pressure pushes the diaphragm along with the plunger down and the pump starts working again.
Bellow type
In this pump instead of a diaphragm, a flexible metal bellow is used. the pump works in the same way as stated for the diaphragm type.
Precautions
Precautions to be taken for the electric fuel pump :
- Don’t connect the battery in reverse polarity.
- Make a correct electrical connection on the fuel pump.
- Don’t drop the fuel pump.
- Never keep the terminal loose.
- Don’t apply overvoltage.
- keep fuel line joint completely close there should be no leakage.
- Don’t install the fuel pump near high temperature.
Fuel pump troubleshooting
Note:- if your vehicle’s fuel pump supplies less fuel, so read carefully this table below.
| Possible causes | Remedies |
| Blocked vent screw on the fuel tank. | Clean the vent hole. |
| Choked or bent fuel pipe from the tank to fuel pump or fuel pump to carburetor. | Clean the pipe remove the sharp bend or replace the squeezed pipe. |
| loose petrol pipe connection. | Tighten the unions. |
| Choked petrol strainer in fuel pump or tank. | Clean the strainer. |
| Loose filter housing on the fuel pump. | Tighten it fully. |
| Broken or pressed filter housing packaging. | Replace with a new one. |
| Leaky diaphragm. | Replace diaphragm. |
| Valve holding clip lose. | Tighten it fully. |
| Leaky valve. | Reface if split valve otherwise changes. |
| Rocker arm pin moved out of its place or worn-out pin. | Reposition the pin and lock it; if worn out replace it. |
| Worn-out rocker arm. | Rebuild or replace. |
| Loose body screw | Tighten it fully. |
| Thick gasket used for mounting fuel pump to block. | Use a thinner gasket. |
We hope readers can understand this “Most Common Fuel Supply System in Petrol Engine” article and basic fundamentals of the fuel supply systems.
Read this:- What is CNG? and Why we should use CNG in India?
Visit site:- www.carsuffer.com






Comment on “Fuel Supply System in Petrol Engine [Spark Ignition Engine]”