In this automobile knowledge-based article we describe the complete working process of the 4-stroke diesel engine with a diagram.
carsuffer.com
The 4-Stroke Diesel Engine is a “Compression ignition” engine (C.I. ENGINE ) is usually called a diesel engine. name after Dr. Rudolf diesel who invented this in the year 1897.
Using fuel with higher specific gravity and less volatile and therefore less inflammable.
In 4-Stroke Diesel Engine only air is charged in the cylinder through inlet valve.
In the diagram of 4-Stroke Diesel Engine compression stroke when both valve or close this air is compressed due to this its temperature rise and before the Piston reaches the top dead center(TDC), diesel fuel is injected into the combustion chamber in fine atomize form.
When this atomize spray comes in contact with hot compressed air the ignition takes place.
In this engine spark plug for ignited the fuel are not provided the fuel which is in atomize form get ignited due to the high temperature of compressed air.
That is why it is know as Diesel compression ignition engine(c.i. Engine).
These Engine are available in both 2-stroke and in 4-stroke cycle.
4-Stroke Diesel Engine Working Diagram
Suction or Induction stroke:-
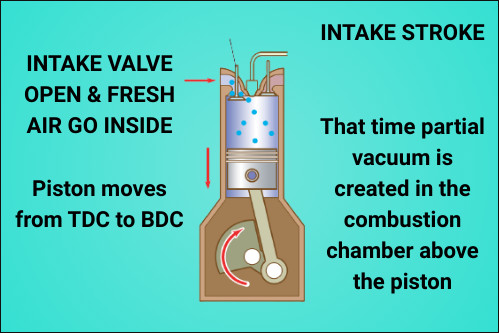
When the piston moves from TDC to BDC the intake valve opens and due to the piston movement downward that time partial vacuum is created in the combustion chamber above the piston.
Due to this partial vacuum, the air is sucked in at the end of the stroke the intake valve closes.
Compression stroke:-
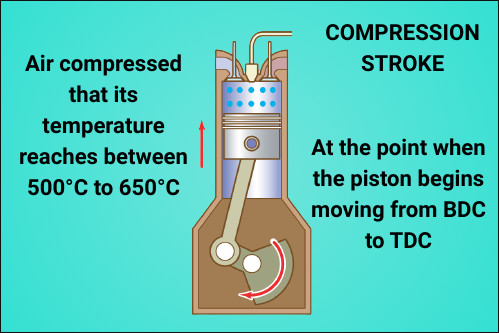
At the point when the piston begins moving from BDC to TDC, the mistake which has been caught in the chamber begins getting a pack.
When the piston reaches near TDC the trapped air gets so compressed that its temperature reaches between 500°C to 650°C.
These higher increases in temperature are because of the higher compression ratio in this stroke both valves remain closed.
Power stroke:-
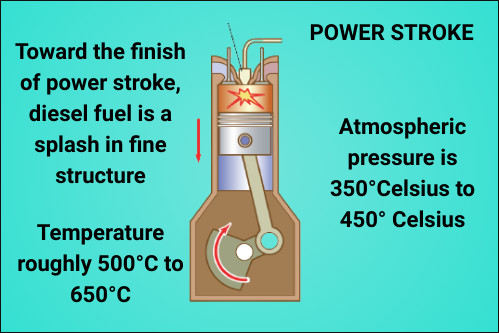
Toward the finish of power stroke, diesel fuel is a splash in fine structure to the consuming hot air which has accomplished temperature of roughly 500°C to 650°C.
Here we would like to mention that the self-ignition temperature of diesel fuel at atmospheric pressure is 350°Celsius to 450° Celsius and atomized fuel in hot air gets ignited in more or less rapid explosion making gases expand.
Exhaust stroke:-
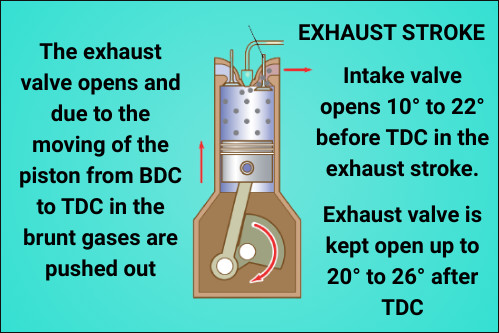
In this stroke, the exhaust valve opens and due to the moving of the piston from BDC to TDC in the brunt gases are pushed out.
In the above-stated strokes, we have seen that the inlet valve opens in suction stroke but as a matter of fact it opens 10° to 22° before TDC in the exhaust stroke.
So valve is completely open when Piston begins going down and enough time is offering for to get in also intake valve stays open in pressure stroke 20° to 30° after BDC.
This indeed is to permit blunder which was coming to a chamber with more prominent speed to feel the chamber totally.
The exhaust valve opens 56°C before TDC in power stroke.
This early opening is specially made to reduce pressure on the Piston top and also to give sufficient time for exhaust gases to find their way out.
Similarly, the exhaust valve is kept open up to 20° to 26° after TDC in the suction stroke firstly to give sufficient time to exhaust gases to clear out
Secondly the fresh air in the exhaust gases out.
Construction of 4-Stroke Diesel Engine.
The Construction of a 4-Stroke Diesel Engine is mechanically similar to the petrol engine but somewhat heavier in construction.
Since they have to stand high pressure and temperature developed due to high compression ratio.
Control System of 4-Stroke Diesel Engine
The 4-Stroke Diesel Engine controls the speed and the power output of the diesel engine are controlled by the quantity of full fuel injected into the cylinder.
While studying the petrol engine it was seen that speed of the engine was controlled by the amount of air admitted into the Carburetor various in diesel engines speed is controlled through controlling the quantity of fuel injected.
You have studied that during Intake stroke only air enters the cylinder as such the quantity of air is constant.
4-Stroke Diesel Engine Combustion Process
In a 4-Stroke Diesel Engine, there is continuous combustion during the engine length of the power stroke and pressure resulting from combustion remains approximately constant throughout its stroke.
The 4-Stroke Diesel EngineEngines are also known as constant volume combustion engines.
Read this:- What is 4-Stroke Petrol Engine & Working of 4-Stroke Petrol Engine
Read this:- How Does a 2-Stroke Diesel Engine Work Explain With Picture
Read this:- What is a 2-Stroke Petrol Engine & the Working of a 2-Stroke Petrol Engine?
Visit site:- www.carsuffer.com






Comments on “4-Stroke Diesel Engine Diagram Explain With Pictures”